NVIDIA lauches next-gen with Vera Rubin
NVIDIA Rubin GPU
NVIDIA Rubin marks a major leap forward in AI computing, designed to meet the explosive demands of next-generation artificial intelligence.
In comparable HGX configurations, Rubin can achieve up to 3.5x higher inference performance, allowing organizations to process more AI queries with fewer GPUs. This performance gain directly translates into higher throughput, faster response times, and improved infrastructure efficiency, especially for AI services running continuously in production environments.
Why choosing Rubin generation?
AI is evolving rapidly from reactive models that generate responses to agentic systems that operate continuously, interact with environments, and make sequence-based decisions.
NVIDIA Rubin is built for this new era of intelligence, providing the infrastructure needed to support internal reasoning, multi-agent coordination, and long-context workflows.
 Courtesy of NVIDIA.
Courtesy of NVIDIA. Courtesy of NVIDIA.
Courtesy of NVIDIA.Efficiency and cost
By improving performance per watt and reducing the cost per generated token, Rubin enables data centers to run advanced AI workloads while controlling energy consumption and operational costs.
For enterprises and cloud providers, this means a more sustainable and financially viable path to deploying large-scale AI, even as model sizes and usage volumes continue to grow.
Architecture and technology
With next-generation Tensor processing, ultra-high-bandwidth HBM4 memory, and high-speed NVLink connectivity, Rubin ensures that data moves efficiently across GPUs with minimal latency.
This tightly integrated architecture is essential for modern AI models that rely on massive parallelism and fast data exchange to deliver accurate, real-time results.
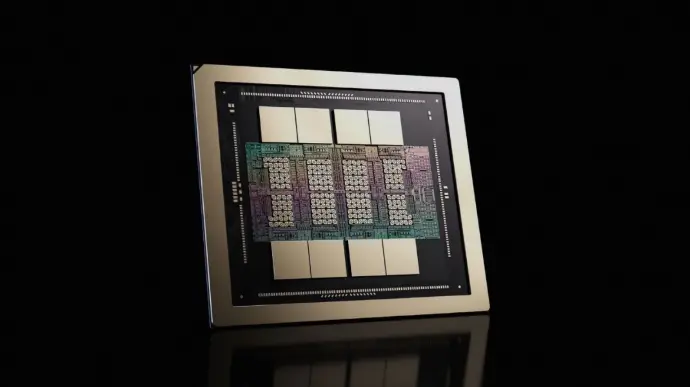 Courtesy of NVIDIA.
Courtesy of NVIDIA.Rubin vs Blackwell
While Blackwell remains a powerful and versatile GPU platform for AI training and inference, Rubin pushes the boundaries further for AI reasoning and large-scale inference.
Rubin is tailored for environments where inference workloads dominate, AI agents operate continuously, and performance efficiency directly impacts business outcomes.
Feature | NVIDIA Rubin NVL8 |
NVIDIA Blackwell HGX B300
|
Form Factor | 8x NVIDIA Rubin SXM | 8x NVIDIA Blackwell Ultra SXM |
INT8 Tensor Core
| 2 PFLOPS | 3 POPS |
FP16/BF16 Tensor Core
| 32 PFLOPS |
36 PFLOPS |
TF32 Tensor Core
| 16 PFLOPS |
18 PFLOPS |
FP32
| 1040 TFLOPS |
600 TFLOPS |
FP64/FP64 Tensor Core
| 264 TFLOPS |
10 TFLOPS |
Total Memory
| 2.3 TB | 2.1 TB |
NVIDIA NVLink
| Sixth generation |
Fifth generation |
NVIDIA NVLink Switch
| NVLink 6 Switch |
NVLink 5 Switch |
NVLink GPU-to-GPU Bandwidth
| 3.6 To/s |
1.8 To/s |
Total NVLink Switch Bandwidth
| 28.8 To/s |
14.4 To/s |
Networking Bandwidth
| 1.6 To/s |
1.6 TB/s |
FP32 SGEMM | FP64 DGEMMCore | 3200 TF | 1600 TF | / |
NVFP4 Inference | 400 PFLOPS | / |
NVFP4 Training | 280 PFLOPS | / |
FP8/FP6 Training | 140 PFLOPS | / |
NVIDIA Vera CPU
The NVIDIA Vera CPU is a foundational component of the Rubin platform, built to orchestrate next-generation AI systems at rack scale.
Rather than acting as a traditional general-purpose processor, Vera is designed to manage, coordinate, and secure large-scale AI workloads where GPUs, networking, and system services must operate as a single, tightly integrated supercomputer.
In AI factories and always-on inference environments, Vera ensures that data flows efficiently between compute resources, networking fabrics, and storage, enabling predictable performance and stable operation at massive scale.
Why Vera matters in the Rubin generation?
As AI systems evolve toward agentic and reasoning-based models, CPU responsibilities shift from simple task scheduling to real-time orchestration of complex AI pipelines.
NVIDIA Vera is optimized for this new role. It acts as the control plane of the AI supercomputer, handling workload management, system-level intelligence, and coordination between GPUs and networking components.
This design is essential for AI systems that must run continuously, adapt dynamically, and scale efficiently across entire data center racks.
 Courtesy of NVIDIA.
Courtesy of NVIDIA.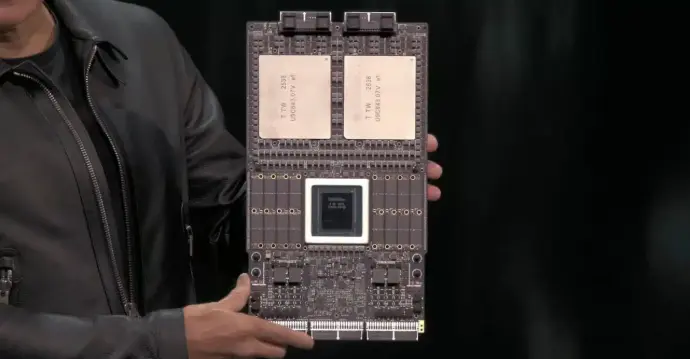 Courtesy of NVIDIA.
Courtesy of NVIDIA.
Vera CPU vs Grace CPU
While Grace CPUs remain highly capable for general AI infrastructure and mixed training–inference workloads, the Vera CPU is purpose-built for the AI inference era introduced with the Rubin platform.
Vera is optimized to orchestrate AI factories, where continuous inference, agentic AI workflows, and long-context reasoning dominate system behavior.
Thermal and power innovations
Energy efficiency is becoming a critical differentiator for AI factories, where up to 30% of power is lost before reaching GPUs due to conversion, distribution, and cooling inefficiencies, so-called parasitic energy.
Every wasted watt increases cost per token and limits AI throughput. The Rubin platform is engineered to minimize these losses, delivering more usable power directly to GPUs through optimized power paths and high-efficiency cooling.
By using warm-water, single-phase direct liquid cooling (DLC) at 45°C, Rubin systems drastically reduce cooling energy, eliminate the need for chilled water, and lower operational costs compared to traditional air-cooled data centers. With nearly double the thermal performance in the same rack footprint, Rubin ensures sustained performance under extreme AI workloads, turning energy savings into higher token output, lower TCO, and improved sustainability.
Interested? Get in touch with our sales team! We have servers and configurations available now.
2CRSi is NVIDIA Elite Partner.


